Diagnostic Audiology Tests
Diagnostic Audiogram
The audiogram is a graph of your hearing loss illustrated in frequencies (pitch) and decibel levels (loudness). Audiometry can be completed using headphones or a soundfield system. There is a component of the test that involves repeating words at increasingly softer volumes, as well as a word list at a comfortable listening level.
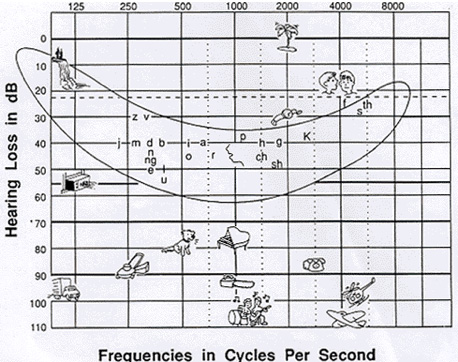
Graph courtesy of: http://www.npcsd.mhrcc.org/local/high_school/Teachers/swunderlich/speech_banana.htm
Tympanometry
Tympanometry is a test where air pressure is presented into the ear canal to test the mobility of the eardrum and is helpful in the detection of middle ear disorders.
Acoustic Reflex Testing
The acoustic reflex is an involuntary muscle contraction in the middle ear. The response is obtained by presenting high intensity sounds via a probe at the opening of the ear canal. The two muscles in the middle ear are the tensor tympani and the stapedius muscle. These muscles contract when high-intensity sounds are presented, and the probe detects the decibel level when the muscles contract.
Auditory Brainstem Response (ABR)
The ABR test measures the speed of electrical impulses traveling along the hearing pathway from the inner ear through the brainstem. The response helps to determine disorders in the hearing pathway.
The test time is approximately one hour. Prior to the test four electrodes are applied: two to the forehead and one on each earlobe, then earphones are inserted into the ear canal. The electrodes pick up electrical responses that appear as waveforms when a series of clicks is presented through the earphones. There is no response needed to the stimulation. It is important that the person being tested is very still and may even sleep through the test.
Videonystagmography (VNG)/Electronystagmography (ENG)
The VNG/ENG is a test designed to help your physician identify the source of your dizziness or imbalance. Dizziness and balance are assessed by using either high-tech video goggles or electrodes placed around your face. Both devices monitor eye movements. There are several tasks to perform including: following a light with your eyes, moving your head and body into different positions and stimulating the balance system with warm and cool air. There are specific medications that need to be discontinued prior to the performance of the test. Medications such as anti-dizziness medications, depressants of any type, antihistamines, as well as alcohol and caffeine may have an impact on the outcome of the balance testing.
Otoacoustic Emissions (OAE)
OAEs are a faint acoustical signal sent from the outer hair cells in the cochlea in response to a stimulus. They are measured by a probe placed at the opening of the ear canal. The emissions are a very soft response and are strongly affected by noise from the patient or in the environment. There is no participation necessary for the completion of the test.
Electrocochleography (ECoG)
The ECoG measures the electrical potentials of the cochlea, which is your organ of hearing. A small electrode is placed into your ear canal along with an earphone. Three electrodes will also be applied: one on your forehead and one on each earlobe. Clicks will be presented through the earphones and the electrical responses will be measured by the electrodes.

